Environmental Sustainability
Water Usage and Recycling
Wafer Works' water intake has had minimal impact on the local area. Both the Yangmei and Longtan fabs are situated in Taoyuan City. According to the World Resources Institute's "Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas," the areas where Wafer Works operates face a medium to low risk of water resource stress. The Longtan fab draws water from third-party providers (tap water) and utilizes surface water collected from rainwater. This water undergoes sedimentation in settling tanks before being recycled for various purposes. Similarly, the Yangmei fab obtains water from third-party providers (tap water) and licensed underground wells. During the establishment and expansion of our facilities, we had consistently submitted water usage plans, which had been approved by the relevant regulatory authorities. These plans were then evaluated by the Taiwan Water Corporation Second Branch to ensure they meet the required water demand. The water source is drawn from the Shihmen Reservoir, which provided an average water supply of 556,730,000 tonnes annually from 2018 to 2022. According to the 46th issue of the 2023 Taiwan Water Corporation Annual Statistics Report, the total water output from the Second District Management Office was 388,825,012 metric tons. In 2024, the Company's total water withdrawal amounted to 1,996,590 metric tons (756,010 tons +1,240,580 tons), accounting for 0.51% of the total water withdrawal, indicating no significant impact on local water resources.
Air conditioning condensate was recycled for use in scrubbers, equipment water was recovered, facility processing units were adjusted for water reuse, and CT system leakage losses were reduced.
Effluent Discgarge
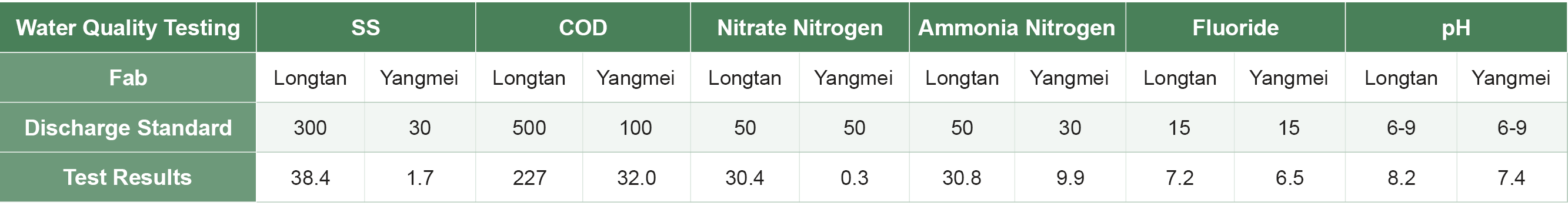
Wafer Works treats all wastewater through proper sewage facilities, ensuring that effluent quality meets the regulatory discharge standards. Regular testing is performed to ensure that the effluent does not significantly impact nearby water bodies. Moreover, Wafer Works has a monitoring and data acquisition system in place to oversee various indices during the wastewater treatment process, including Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Suspended Solids (SS), fluoride concentration (F-), and pH levels. This system allows for immediate action in case of any malfunction, preventing environmental contamination. If abnormal water quality is detected, the monitoring system promptly alerts on-duty personnel to take appropriate measures to prevent violations and environmental pollution. Since its inception, Wafer Works has placed a premium on water pollution prevention and water resource management. We continue to promote water recycling initiatives annually, striving to reduce water consumption and protect water resources.
During the reporting period, Wafer Works' water intake was 756.01 million liters for the Yangmei fab and 1,240.58 million liters for the Longtan fab. The total wastewater produced was 708.44 million liters for the Yangmei fab and 1,050.31 million liters for the Longtan fab.
The monitored values of water intake and discharge for Wafer Works' Longtan and Yangmei fabs during the reporting period are as follows:
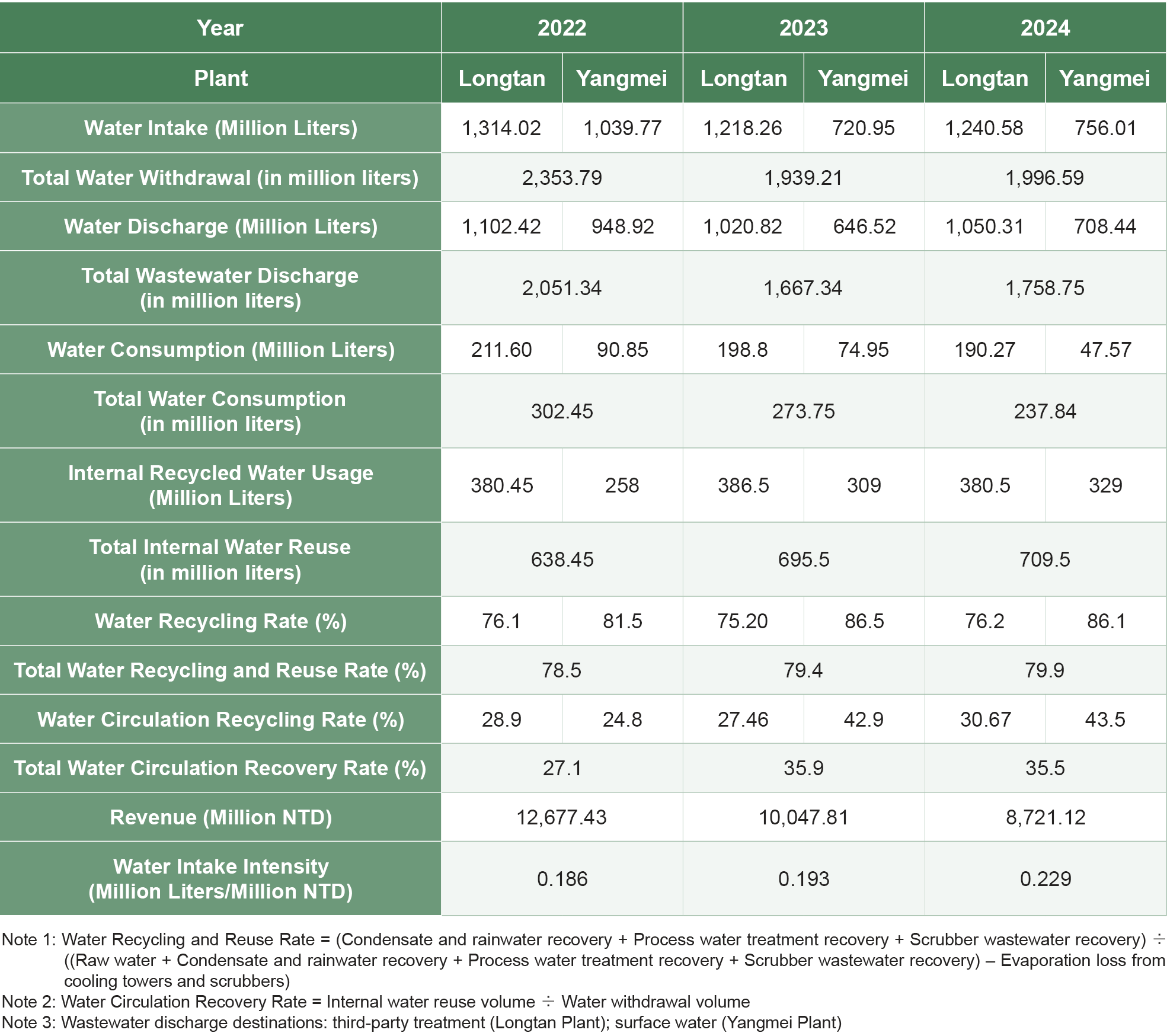
Water Recycling Rate

Water Circulation Recycling Rate

Energy Management and Policy

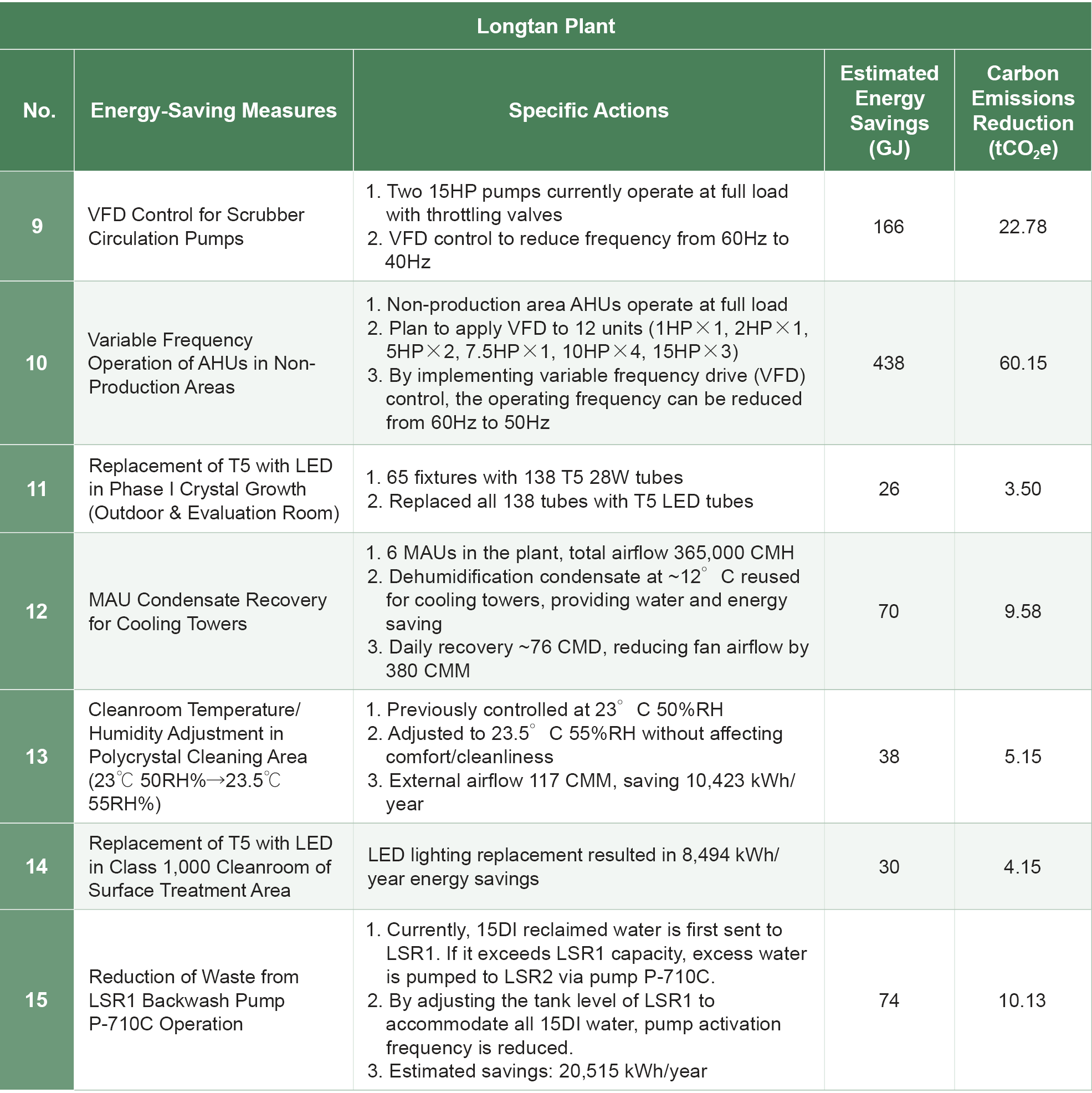
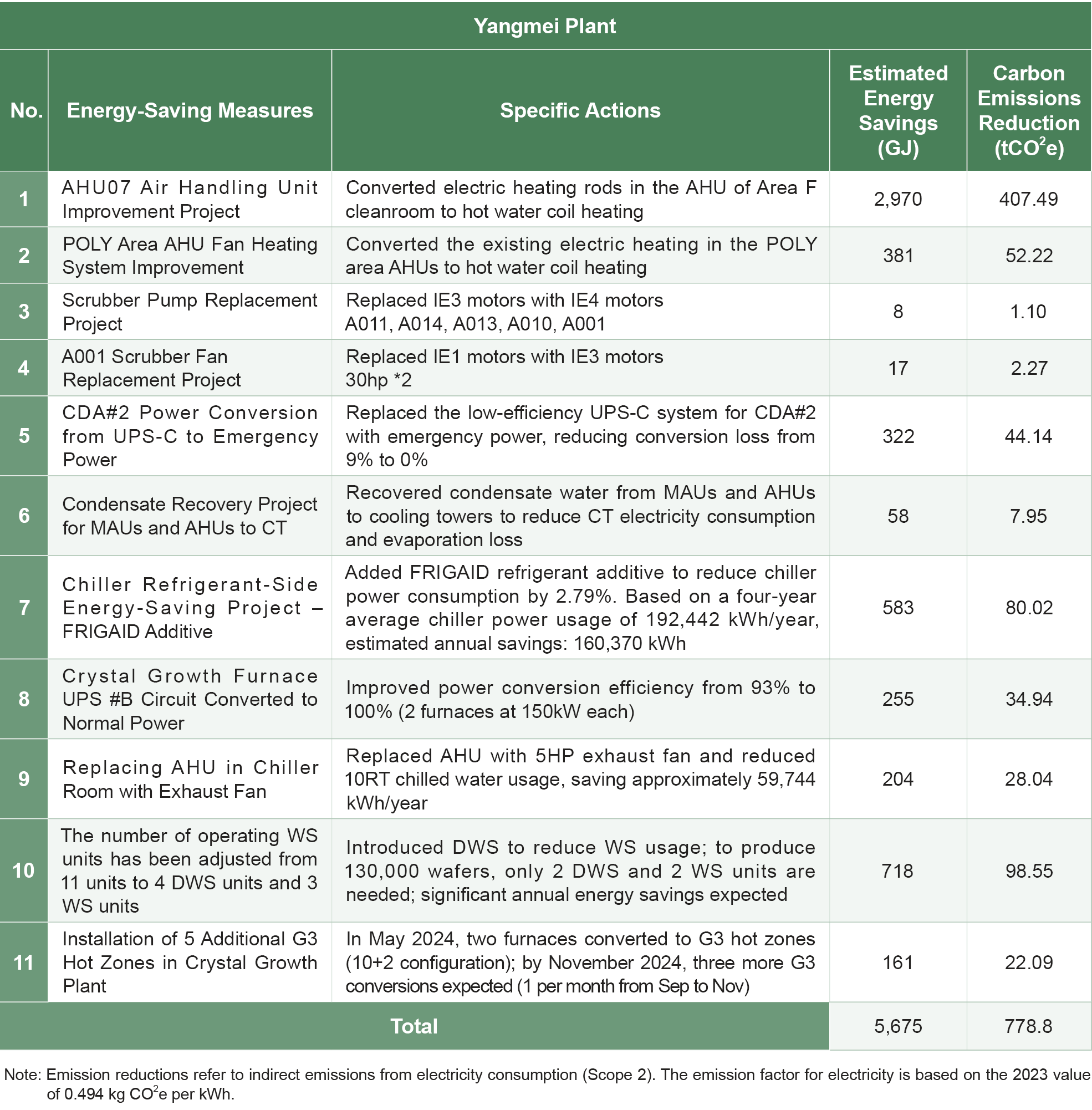
The energy usage of Wafer Works' Longtan Plant during the reporting period is shown in the table below. In 2024, the Longtan Plant saved 1,800,485 kWh of electricity, reducing energy usage by 6,482 GJ with an energy-saving rate of 2.2%. In the same year, the Yangmei Plant saved 1,576,519 kWh, reducing energy usage by 5,675 GJ, with an energy-saving rate of 4.0%.
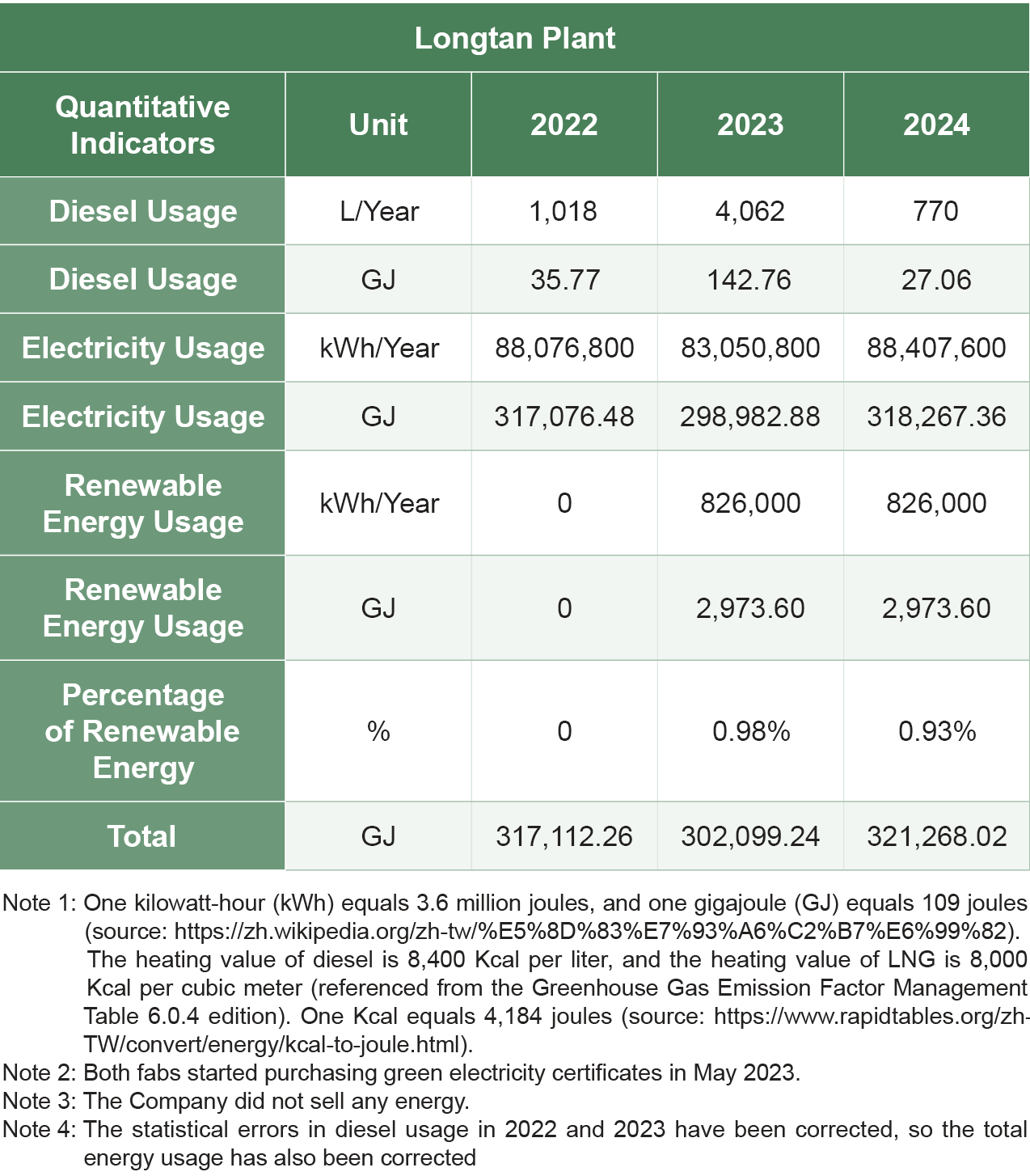 |
 |
Energy Intensity
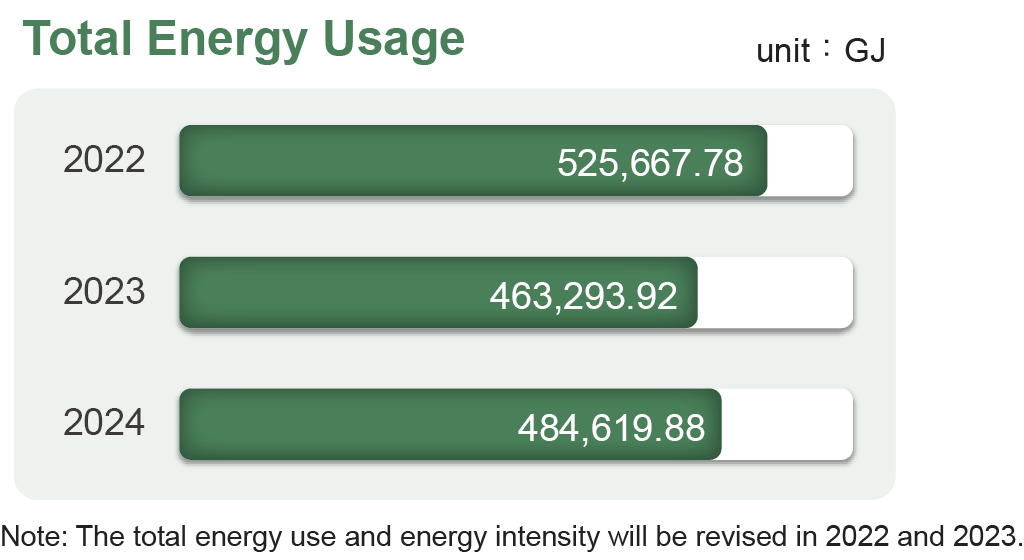 |
 |
Energy Saving Achievements
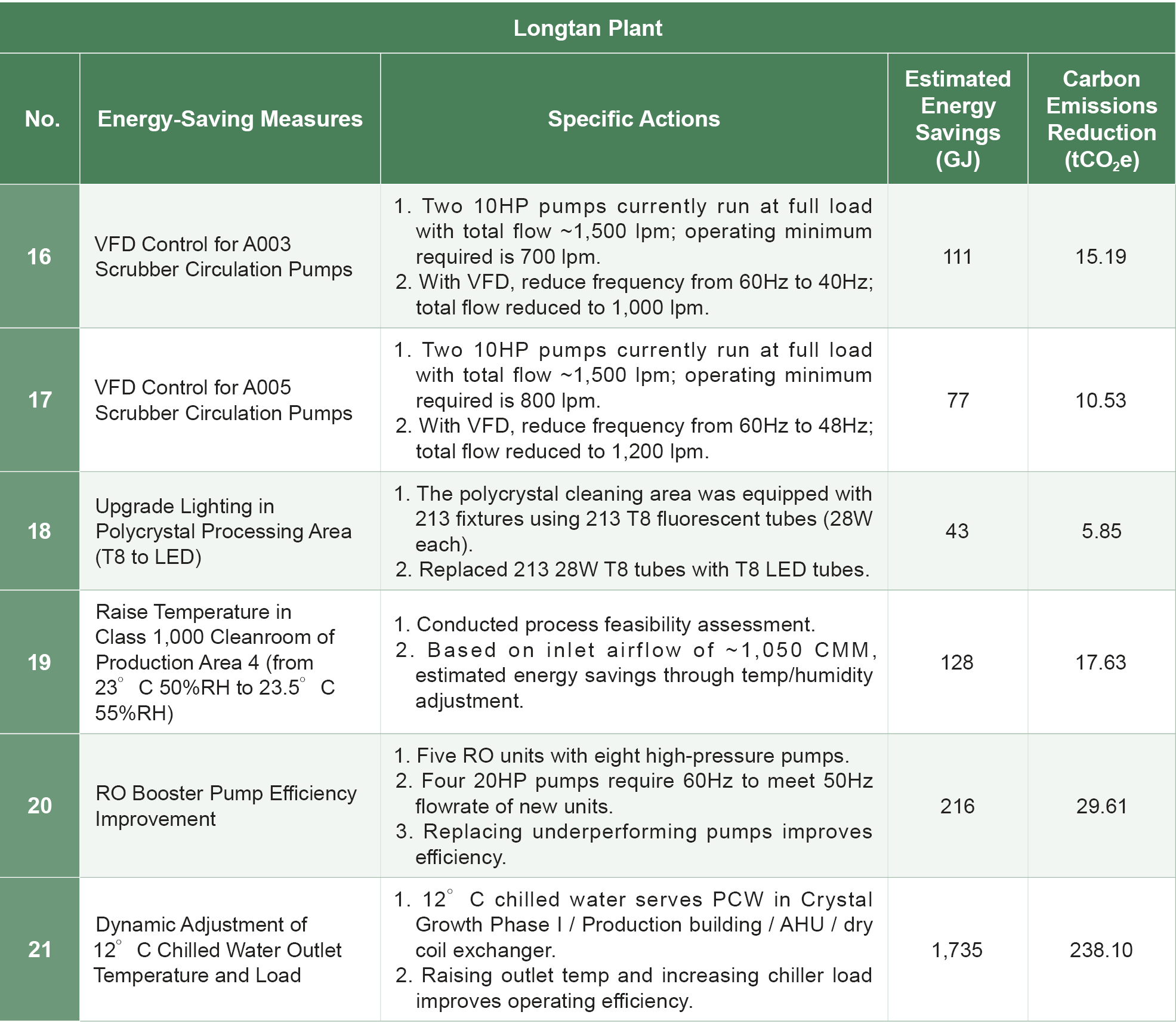
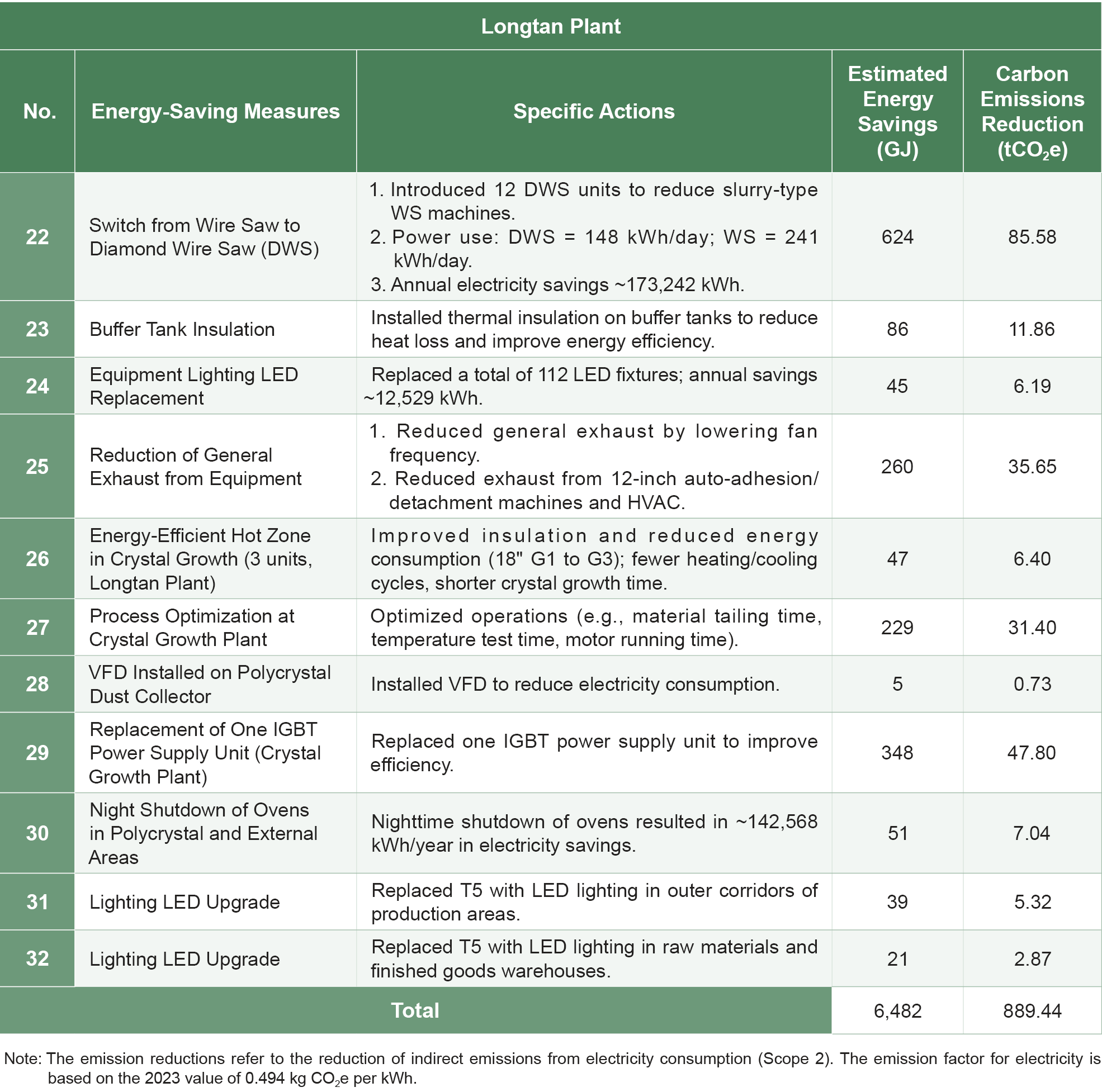
Climate Change Response
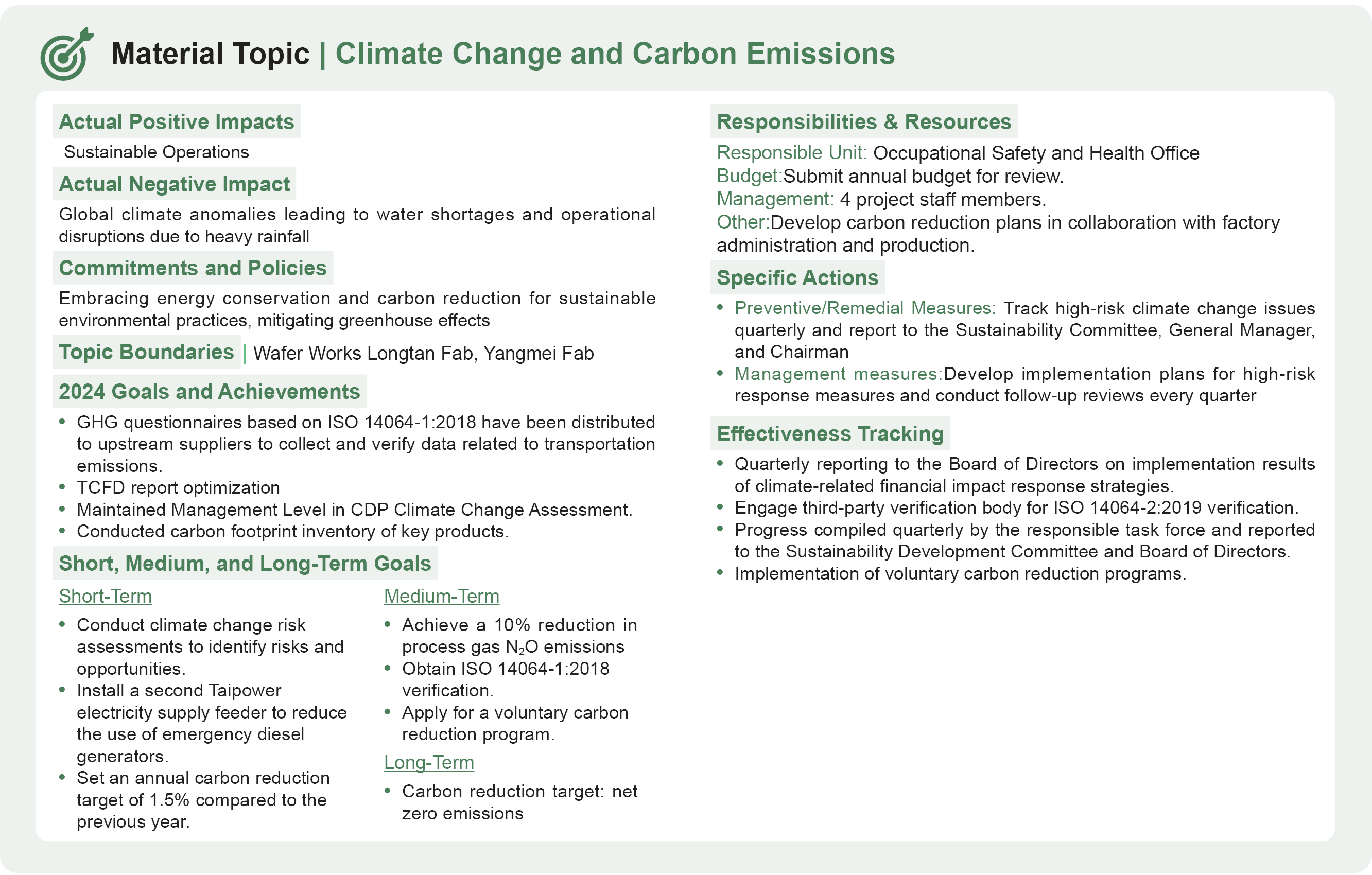
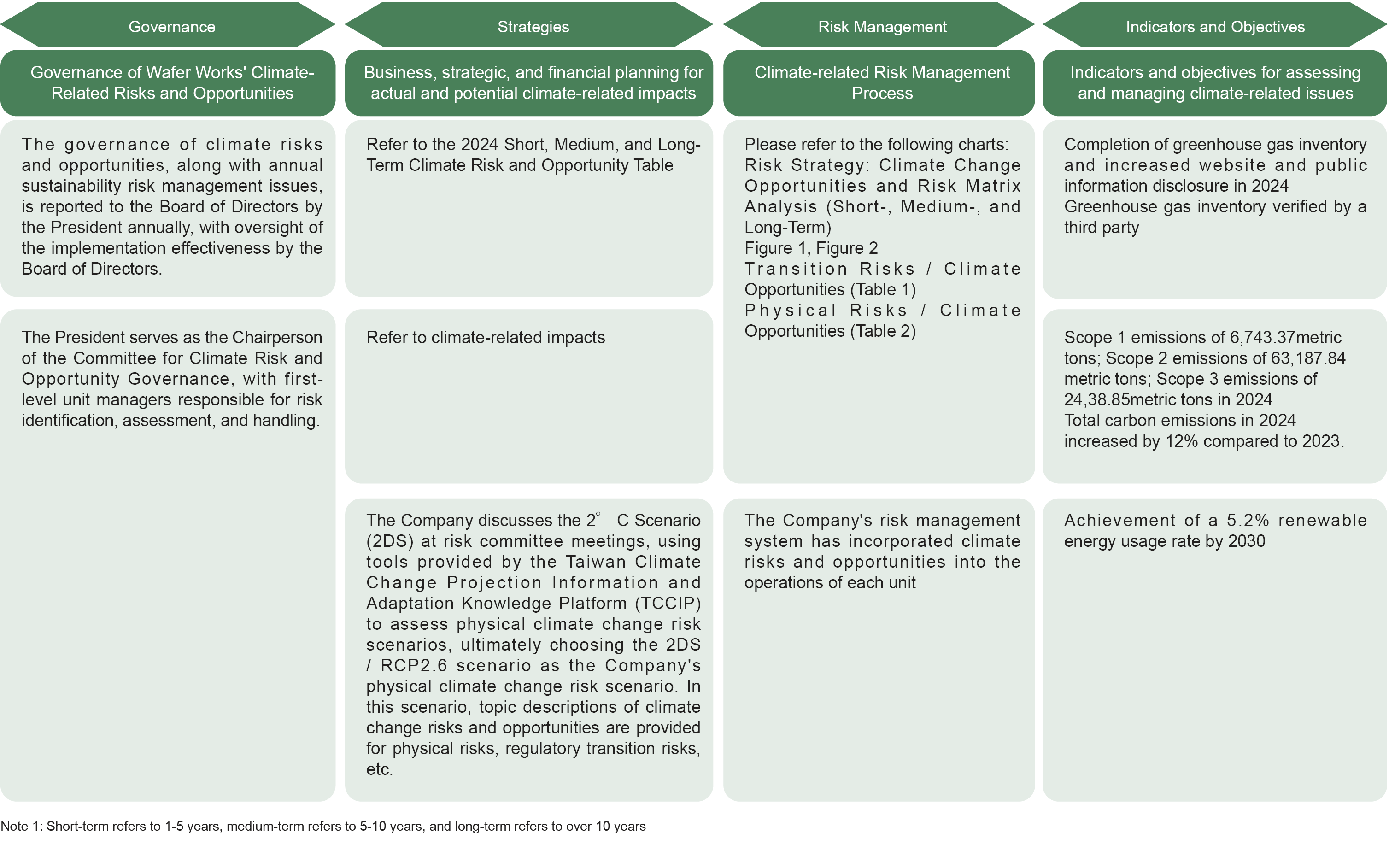
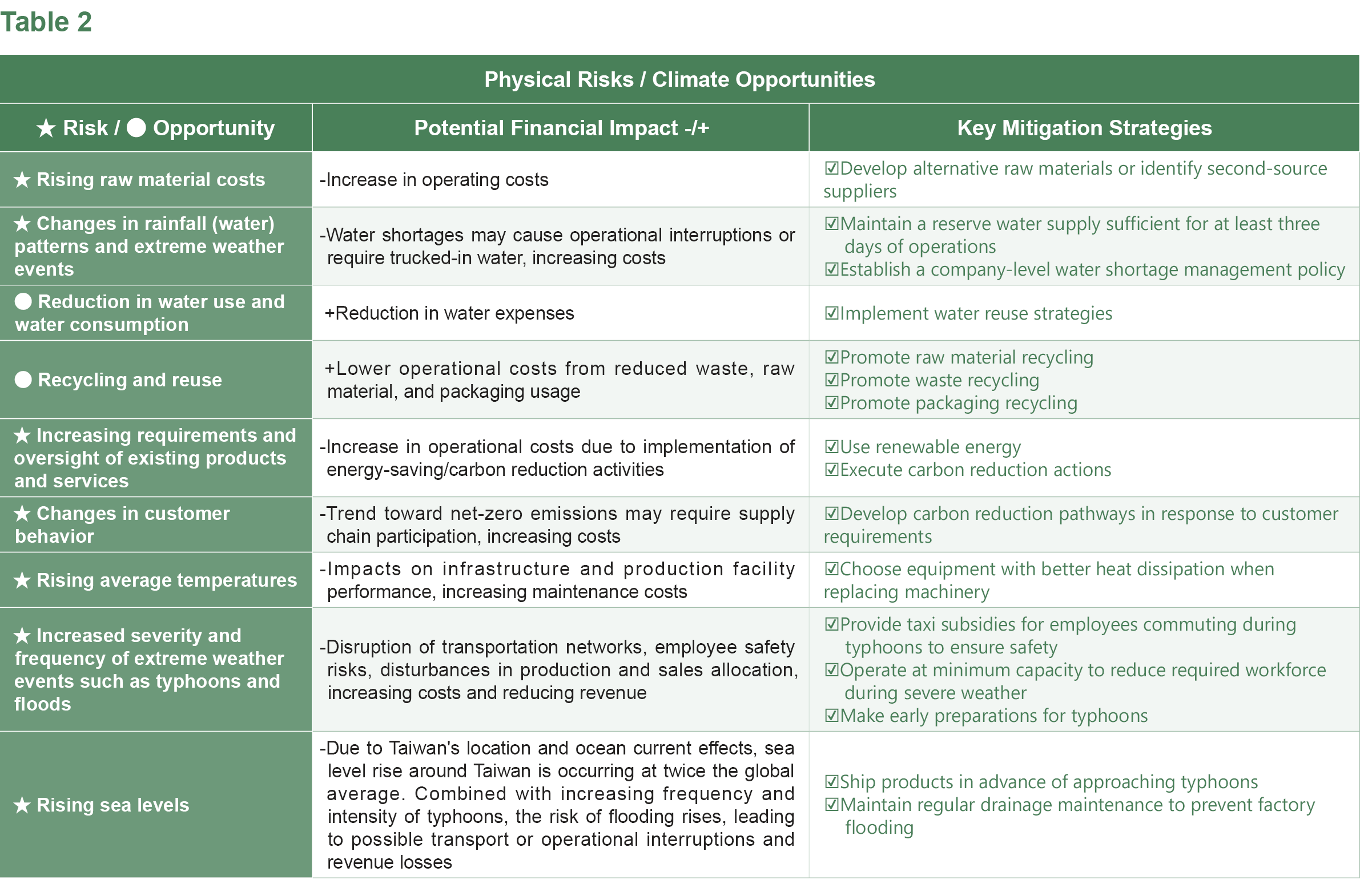
Wafer Works has established internal control and audit systems, as well as risk management measures. Due to global warming leading to extreme weather events and the rising awareness of environmental conservation, energy efficiency, safety, and health, the Company has striven to fulfill its corporate social responsibility to establish a foothold in the industry. Following the framework of the Task Force on Climate related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), Wafer Works' response can be categorized into governance, strategy, risk management, indicators, and targets. Sustainable Development Committee members identify climate related risks and opportunities, formulate response strategies, and report to the Board of Directors annually. The Board of Directors oversees the effectiveness of implementation.
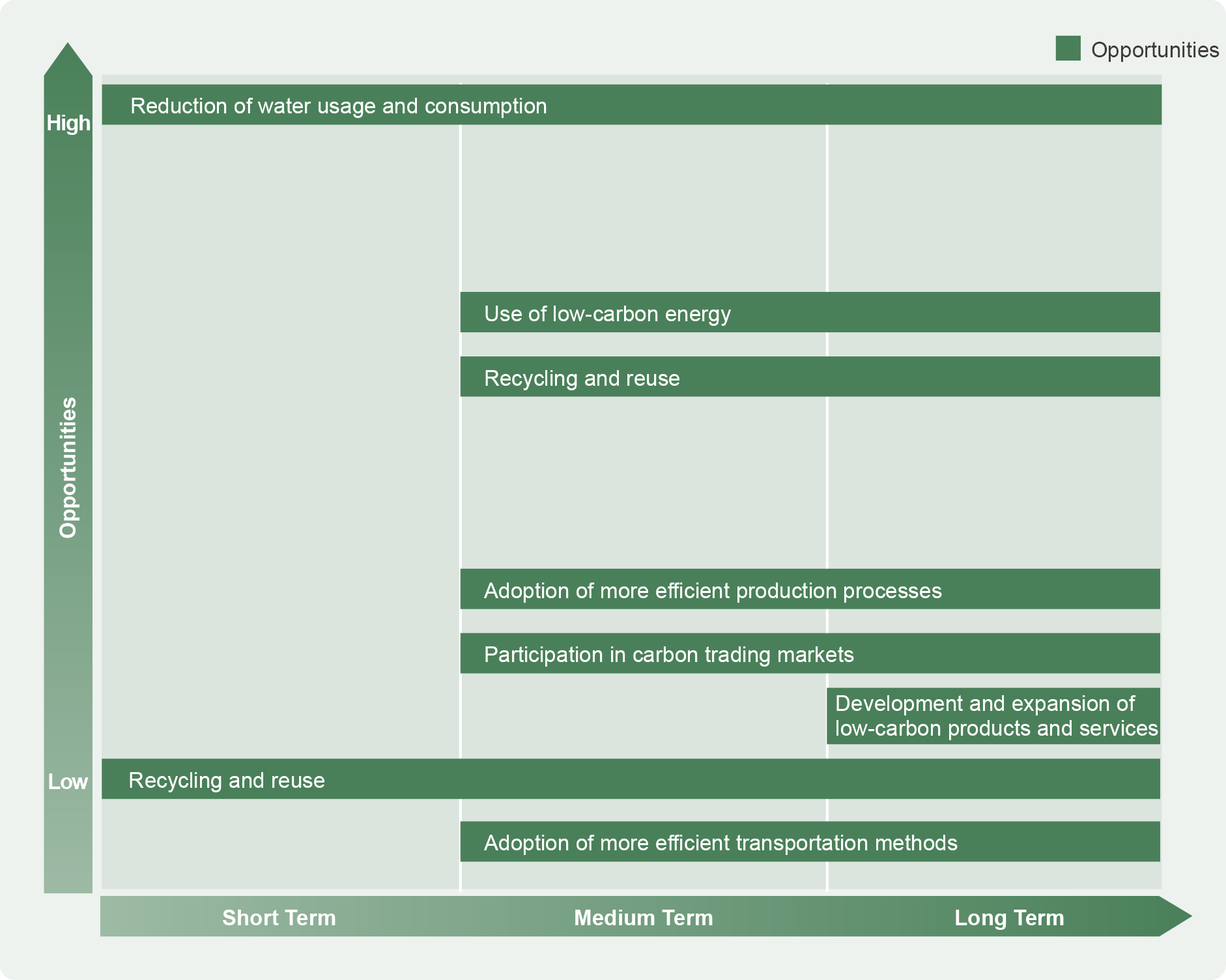
Risk Strategy: Climate Change Opportunities and Risk Matrix Analysis (Short-, Medium-, and Long-Term)
 |
 |
Climate-related Impacts

  |
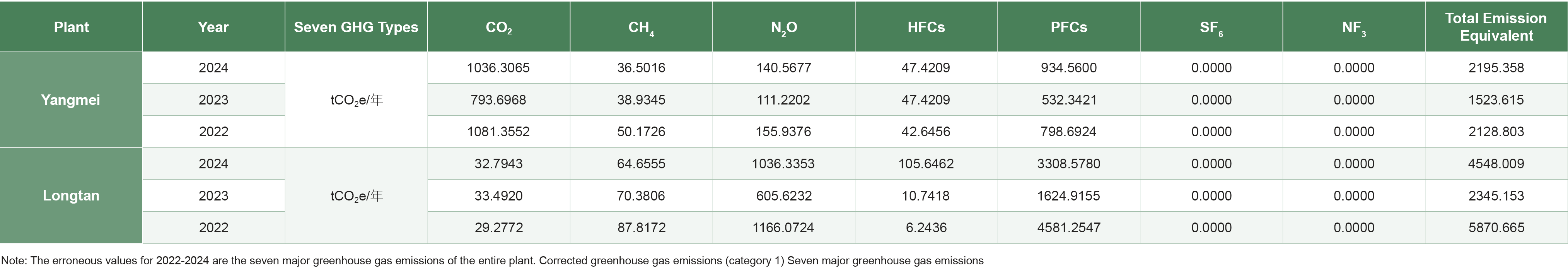
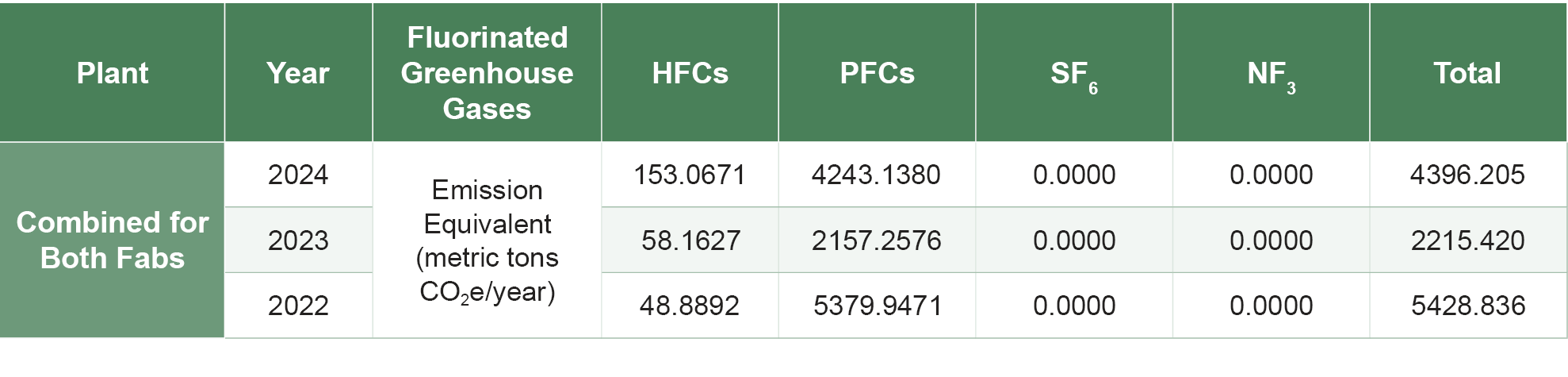
In 2024, Wafer Works' total greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2) amounted to 69,931.21metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent. The primary emissions came from Scope 2 purchased electricity, followed by process emissions, including perfluoropropane (C3F8) and nitrous oxide (N2O). For the first time in 2022, Scope 3 emissions were included in the inventory, primarily focusing on other indirect emissions generated from outsourced activities, with emissions sources owned or controlled by other companies.
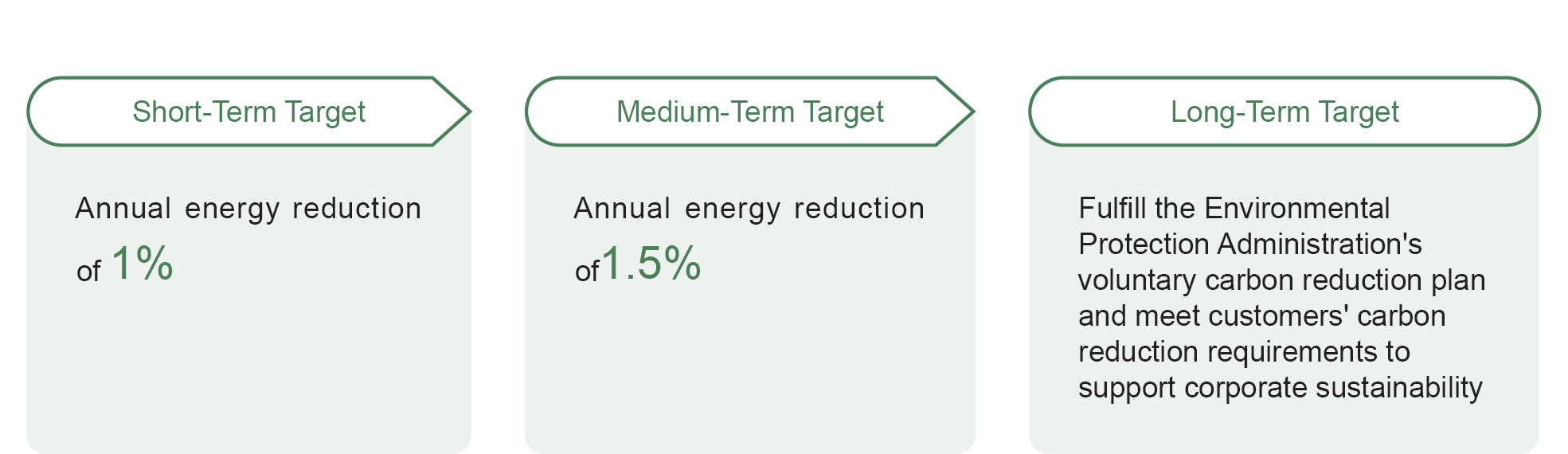
Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions Increased in 2024: Due to the addition of a 12-inch production line at the Longtan Plant, total carbon emissions rose in 2024. In response, the annual energy-saving target was set at 1.5%. The combined energy savings from both plants in 2024 reached a 2.7% reduction compared to the previous year, thereby achieving the carbon reduction target.
Wafer Works Carbon Reduction Goals
The greenhouse gas emissions for the past three years (Scope 1) are as follows:
Total for the Company Emission Intensity
Environment, Health and Safety Policy

Wafer Works has established operation and maintenance procedures for air pollution control, water pollution prevention, and waste management. Relevant departments strictly adhere to these procedures to ensure all facilities operate at maximum efficiency. Various monitoring systems are installed at the discharge points of pollution control facilities. If monitoring values exceed alarm thresholds, operators will follow emergency response and notification procedures to address the issue immediately. Each year, we carry out emergency response drills for air and water pollution control and enhance internal environmental awareness to prevent environmental pollution and legal violations. Under this comprehensive pollution control monitoring and management system, Wafer Works did not contravene any environmental regulations from 2022 to 2024.

Air Pollution Control
Wafer Works' strategy for air pollution control starts by optimizing processes to minimize the introduction of pollutants into exhaust gases. Subsequently, high-efficiency equipment is deployed to treat pollutants within the exhaust, guaranteeing compliance with government standards regarding the level of pollutants emitted into the atmosphere. Wafer Works classifies emissions into alkaline exhaust, acidic exhaust, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The air pollution control equipment varies based on the type of pollutants being treated, and all emissions comply with the regulations set by the Environmental Protection Administration. Wafer Works also prioritizes the rights of neighboring companies and community residents. All equipment operations are centrally monitored by staff on a 24-hour rotating schedule. Continuous monitoring devices are installed to track VOC emission
concentrations. Any variations in operating conditions are under constant monitoring, and if they deviate beyond the preset limits, an immediate alert is sent out.
Circular Economy and Waste Management
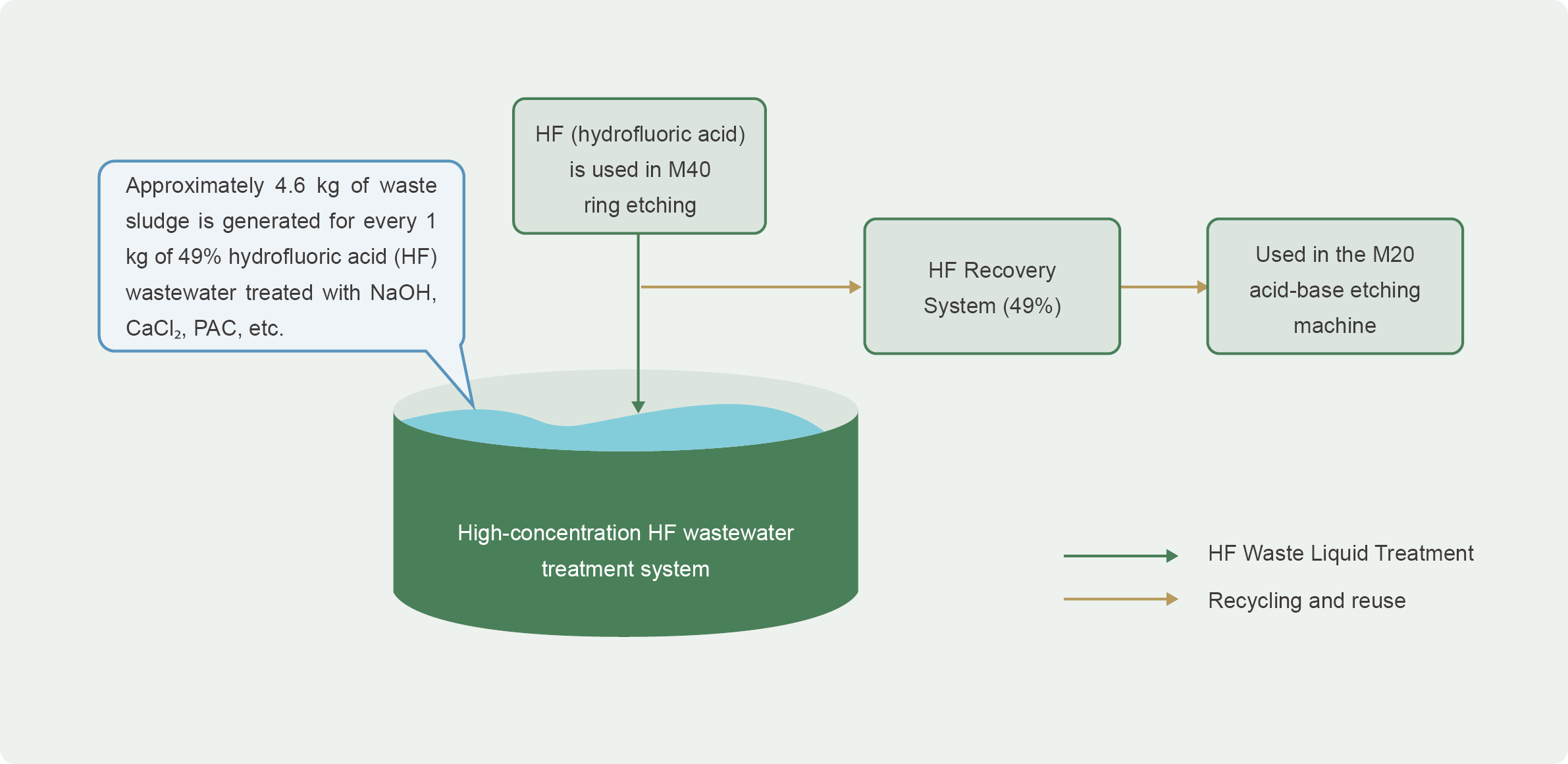
Wafer Works adheres to a circular economy reuse model. In 2024, the Company promoted waste reduction at the source and circular resource utilization through the implementation of ISO 59004:2024 circular economy guidance (focused on waste acid reuse). The optimization of the waste acid recovery system enabled the 2024 hydrofluoric acid (HF) recycling project, in which HF used in the surface treatment process (etching equipment) was recovered and reused in the forming process (acid-alkali etching machines), achieving both waste and carbon reduction benefits. In 2024, a total of 12,320 liters of HF was recycled, resulting in cost savings of approximately NT$2,052,407 (including chemicals, sludge treatment, and raw materials). The reduction in HF production emissions amounted to 48.541 tCO2e (based on a carbon footprint of 3.94 kgCO2e per liter of HF; source: Product Carbon Footprint Information Platform). ISO 59004:2024 certification for this program is expected to be obtained in 2025. (Picture 1)
Broken wafer recycling accounted for 34.91% of total production capacity, while recycled crystal ingot top and tail waste and crucible bottom material represented 14.03% of total input volume. In 2024, the Company continued to maintain performance in these operations, contributing to ongoing waste reduction and circular resource use.
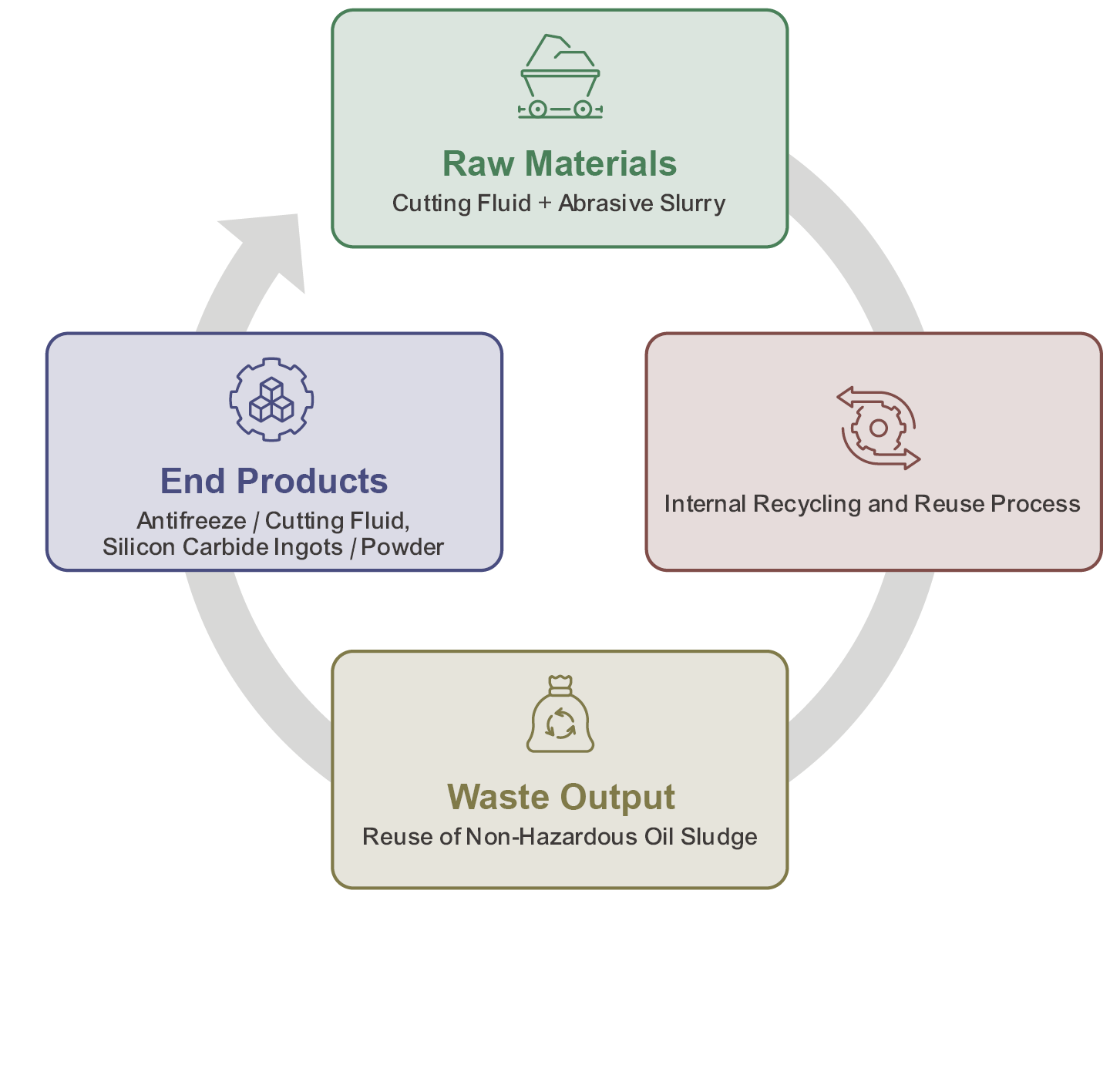
Wafer Works has an established waste treatment and recycling mechanism. Waste is strictly categorized, and a dedicated team monitors the waste storage areas to oversee disposal practices. Regular waste-sorting awareness training is provided to all employees, from new hires to existing staff. By implementing comprehensive controls from the source to the point of disposal, the Company reduces carbon emissions associated with incineration. Aligned with circular economy principles that emphasize source reduction, Wafer Works has developed a cutting fluid recycling system for wafer slicing processes, which are carried out using two methods. The first method, steel wire slicing, utilizes a combination of cutting fluid and abrasive slurry. It relies on the tension of steel wires and the friction of abrasive particles to cut silicon ingots into wafers. The resulting waste is classified as non-hazardous oil sludge. Since the slurry retains its process suitability after initial use, centrifugal separation is employed to remove non-conforming particles. The recovered slurry is mixed with fresh material and returned to the production line. Discarded slurry is sent to qualified recyclers for conversion into silicon carbide ingots or powder, which can be reused in steel plants as heating agents or by refractory material manufacturers. Cutting fluid can also be distilled using its boiling point properties and repurposed as antifreeze in colder climates. (Figure 2) The second method, diamond wire slicing, requires only cooling fluid, thereby reducing both material use and waste generation. As the Company gradually phases out steel wire machines in favor of diamond wire machines, it is estimated that full replacement will save approximately 301.49 metric tons of cutting fluid and slurry and reduce non-hazardous oil sludge waste by 534.43 metric tons annually.
Reusable industrial waste includes sludge, oil sludge, chemical drums, quartz crucibles, graphite crucibles, blue protective films, pallets, and other materials recyclable waste materials such as paper, PET bottles, iron, aluminum cans, recyclable plastics, styrofoam, and metal scraps are sorted and collected, then handed over to certified local waste treatment companies. Non-recyclable waste is disposed of as general waste by certified waste removal vendors and transported to government designated incineration facilities.
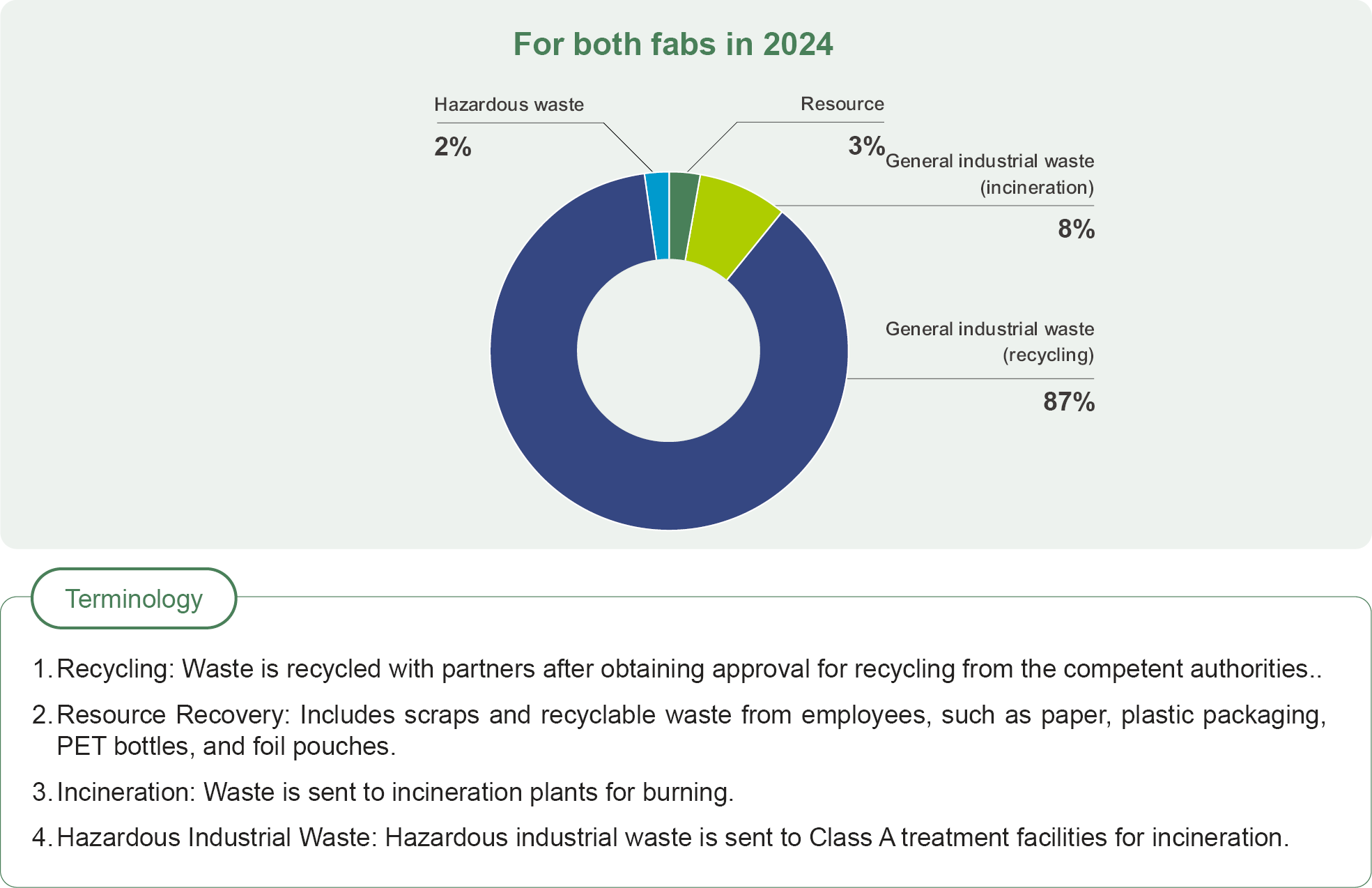
Wafer Works produces several types of industrial waste: general industrial waste, hazardous industrial waste, empty chemical containers, and recyclable waste. All waste is stored and transported according to legal regulations.
The methods for disposing of industrial waste at Wafer Works are as follows: 87% recycling, 8% incineration, and 2% resource recovery. Please refer to the waste disposal method distribution chart for detailed information. Wafer Works focuses on reducing pollution and managing waste through recycling initiatives. The primary source of hazardous industrial waste is empty chemical containers that contain chemical materials during the manufacturing process. These containers undergo regular annual audits, and each waste shipment is tracked with manifests to collect and monitor related data. The 86% recycling rate includes both general and hazardous industrial waste. In 2023, Wafer Works managed hazardous industrial waste, including empty chemical barrels, through a partnership with recycling processors. The process involves cleaning, neutralization, testing, certification, shredding, and recycling the plastic, with approval from regulatory authorities.